Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) has become a cornerstone in the detergent industry, owing to its exceptional properties that enhance cleaning efficiency. This article provides a comprehensive overview of CMC’s role in detergents, tracing its historical development and delving into its chemical properties that make it a preferred choice in stain removal.
CMC, a water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose, is extensively used as a key ingredient in both liquid and powder detergents. CMC Detergent primary function is to act as a soil suspension agent, which prevents re-deposition of dirt on fabrics during the wash cycle. The inclusion of CMC in detergent formulations not only enhances the cleaning efficacy but also improves the texture and stability of the detergents.
The journey of CMC in the detergent sector dates back to the mid-20th century. Its adoption was driven by the need for more effective and fabric-friendly cleaning agents. Over the years, CMC has evolved from a mere additive to a vital component in detergent CMC tables, signifying its crucial role in modern detergent formulations.
This historical progression reflects the industry’s shift towards more efficient, sustainable, and safer cleaning agents. As CMC surfactant properties were recognized, it gradually replaced more traditional, less efficient ingredients. Its ability to function effectively at the critical micelle concentration marked a turning point in detergent development.
In summary, the introduction of CMC in detergents has been a significant advancement in the industry. Its unique properties not only boost cleaning power but also align with the evolving demands for safer and more environmentally friendly products. The subsequent sections will further explore the chemical properties of CMC that contribute to its stain-removing prowess.

Chemical Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose That Enhance Stain Removal
The Molecular Structure of Carboxymethyl Cellulose and How It Interacts with Stains
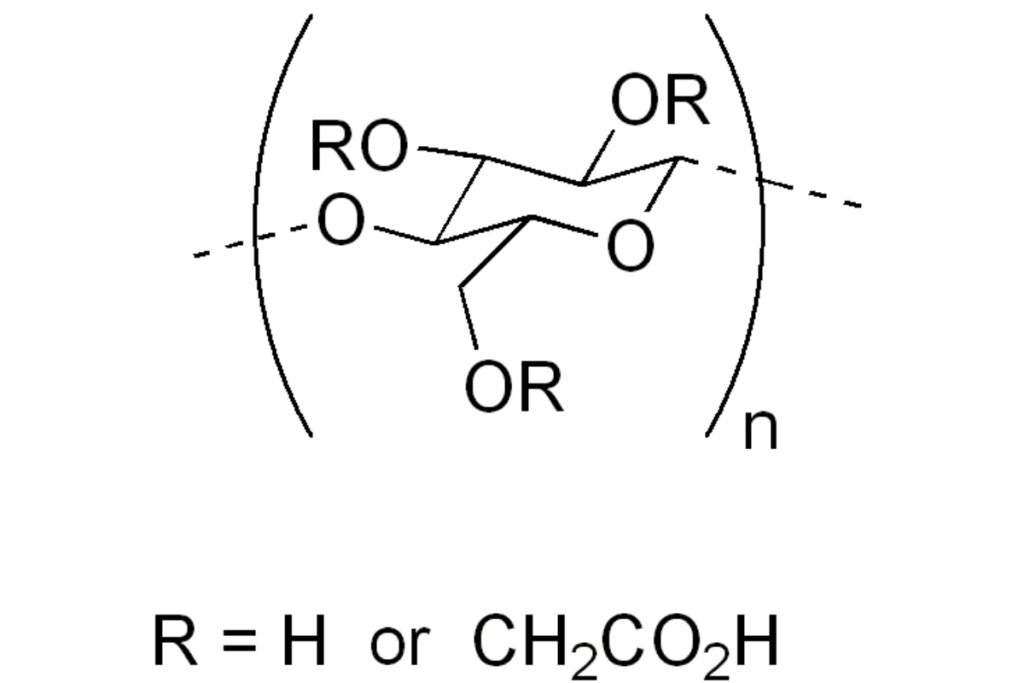
Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC), with its unique molecular structure, plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of detergents. CMC molecules are characterized by long chains of cellulose, which are chemically modified to carry carboxymethyl groups. This modification imparts a negative charge to the CMC molecules, making them highly effective at interacting with and trapping dirt and stain particles.
The interaction between CMC and stains is primarily based on the principle of polarity. Most stains contain oils and proteins, which are non-polar substances. CMC, being polar, effectively binds with these non-polar stain molecules. This action not only helps in loosening the stains from the fabric fibers but also prevents them from reattaching, ensuring a thorough cleaning.
Role of Carboxymethyl Cellulose in Breaking Down and Lifting Stains from Fabrics
CMC’s role in stain removal extends beyond mere interaction with the stains. Once CMC molecules bind with the stain particles, they facilitate the breaking down of these particles. This breakdown is crucial in removing more stubborn or set-in stains, which require more than just surface-level treatment.
Additionally, CMC aids in lifting the broken-down stain particles away from the fabric. In the washing process, the movement of water and mechanical action of the washing machine further enhance this lifting effect. The result is a more efficient removal of stains, leaving the fabrics cleaner and fresher.
The effectiveness of CMC in liquid detergent and detergent powder is due to these chemical properties. Its ability to interact with stains, break them down, and lift them off the fabric makes it an indispensable ingredient in modern detergents. As we delve further into the comparison with other detergent ingredients, the unique advantages of CMC become increasingly evident.
Comparison with Other Detergent Ingredients
How Carboxymethyl Cellulose’s Effectiveness Compares to Other Common Detergent Additives
Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) distinguishes itself from other detergent additives through its specific properties and effectiveness. When compared to conventional additives like phosphates (e.g., STPP uses in detergent) and optical brighteners (e.g., Tinopal uses in detergent), CMC offers unique advantages. While phosphates are effective in softening water and aiding in dirt removal, they pose significant environmental concerns. CMC, on the other hand, provides effective soil suspension and anti-redeposition qualities without the same environmental impact.
Optical brighteners like Tinopal work by enhancing the appearance of fabrics but do not contribute to the actual cleaning process. In contrast, CMC plays a direct role in removing and suspending stains, making it more than just a cosmetic additive. Its functionality is centered on improving the core cleaning performance of detergents.
Advantages of Using Carboxymethyl Cellulose in Terms of Safety and Environmental Impact
The safety and environmental impact of detergents are increasingly important considerations. CMC stands out for its safety profile, being non-toxic and biodegradable. Unlike some traditional detergent ingredients that can be harsh on fabrics and the skin, CMC is gentle, making it suitable for sensitive skin and delicate fabrics.
From an environmental standpoint, CMC is a more sustainable choice. It is derived from renewable plant sources and does not contribute to eutrophication, a common environmental issue associated with phosphates in detergents. The biodegradability of CMC means it breaks down naturally in the environment, reducing the ecological footprint of detergents.
In summary, compared to other common detergent additives, CMC offers a balance of effective stain removal, fabric safety, and environmental sustainability. Its unique properties and safety profile make it a valuable ingredient in modern detergent formulations, catering to the growing demand for eco-friendly and efficient cleaning solutions.

Carboxymethyl Cellulose in Different Types of Detergents
Application of Carboxymethyl Cellulose in Liquid Versus Powder Detergents
The effectiveness of Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) varies in different detergent formulations, particularly between liquid and powder detergents. In liquid detergents, CMC serves as a stabilizing agent that prevents the separation of ingredients, maintaining a consistent texture and efficacy throughout its shelf life. Its solubility in water makes it particularly effective in liquid formulations, where it can quickly interact with stains and soils.
In contrast, in powder detergents, CMC plays a crucial role in the granulation process, helping to bind the detergent particles together. Though less soluble than in liquid form, CMC in powder detergents still effectively aids in soil suspension and stain removal once it is dissolved in the wash water.
Effectiveness of Carboxymethyl Cellulose in Various Water Conditions (Hard and Soft Water)
The performance of detergents, including those with CMC, can be influenced by water hardness. Hard water, which contains high levels of minerals like calcium and magnesium, can impede the cleaning action of detergents. However, CMC’s chemical properties make it particularly adept at functioning in both hard and soft water conditions.
In hard water, the carboxymethyl groups in CMC can bind with calcium and magnesium ions, mitigating the negative effects of water hardness on the cleaning process. This interaction helps maintain the efficacy of the detergent, ensuring effective stain removal and soil suspension.
In soft water, CMC’s properties are maximized, allowing for optimal performance in soil suspension and anti-redeposition. This means that in soft water, CMC-enhanced detergents can perform exceptionally well, providing efficient cleaning with reduced amounts of detergent.
In conclusion, CMC’s versatility in both liquid and powder detergents, coupled with its effectiveness in different water conditions, underscores its importance in the detergent industry. Its ability to adapt to various formulations and environmental conditions makes it a valuable ingredient in enhancing the overall performance of detergents.
The Science of Stain Removal
Detailed Explanation of the Stain Removal Process with Carboxymethyl Cellulose
The stain removal process using Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) in detergents is a fine interplay of chemistry and physics. CMC functions by targeting the stains at a molecular level. When added to a detergent formula, CMC molecules distribute evenly in the wash water, creating a network that traps and suspends soil and stain particles.
At the core of its action, CMC works through a mechanism known as soil suspension. As clothes are agitated in the washing machine, CMC helps loosen the stains from the fabric fibers. Once detached, these stain molecules are enveloped by CMC molecules. This encapsulation prevents the stains from resettling on the fabric, a process known as anti-redeposition.
Additionally, the hydrophilic (water-attracting) nature of CMC ensures that these suspended stain particles are effectively washed away with the rinse water. This action is crucial for thorough cleaning, as it ensures that stains are not just dislodged but also completely removed from the fabric.
Case Studies or Examples Demonstrating Carboxymethyl Cellulose’s Efficiency in Removing Specific Types of Stains
CMC’s efficiency in stain removal has been demonstrated in various case studies. For example, in the removal of oil-based stains, which are notoriously difficult to eliminate, CMC has shown remarkable efficacy. Its molecular structure allows it to penetrate these greasy stains, breaking them down and making them easier to wash away.
Another example can be seen in the treatment of protein-based stains like blood or food. CMC’s effectiveness in these cases lies in its ability to bind to the protein molecules, loosening them from the fabric and suspending them in the wash water.
These case studies underscore the versatility of CMC in tackling a wide range of stains, from everyday spills to more stubborn marks. Its consistent performance across various fabric types and stain categories establishes it as a key component in the science of stain removal, contributing significantly to the efficacy of modern detergents.
Innovations and Future Trends in CMC Detergents
Recent Advancements in Carboxymethyl Cellulose Detergent Formulations
The detergent industry continues to innovate, with Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) at the forefront of many of these advancements. Recent developments in CMC formulations have focused on enhancing its efficiency and environmental friendliness. One such innovation involves modifying the molecular structure of CMC to improve its solubility and effectiveness in cold water washes. This adaptation not only saves energy but also ensures better stain removal in lower temperatures, aligning with sustainable living practices.
Another advancement is the integration of CMC with enzymes in detergent formulations. This combination harnesses the soil-breaking power of enzymes with the soil-suspending abilities of CMC, resulting in detergents that are more effective at lower concentrations. Such formulations are not only cost-effective but also reduce the environmental load, as less detergent is needed per wash.
Future Prospects and Potential Improvements in Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Detergents
Looking to the future, the potential for improvements in CMC-based detergents is vast. One area of focus is the development of biodegradable and eco-friendly variants of CMC. As environmental concerns become more pressing, creating detergents that minimize ecological impact while maintaining cleaning efficiency is paramount.
Additionally, research into tailoring CMC molecules for specific types of stains or fabrics could lead to more specialized detergents. This customization could address the growing consumer demand for targeted cleaning solutions, catering to a diverse range of laundry needs.
The exploration of synergistic combinations of CMC with other sustainable and natural ingredients is also an exciting prospect. Such combinations could enhance the overall performance of detergents while maintaining a commitment to environmental responsibility.
In conclusion, the ongoing innovations and future trends in CMC detergents point towards a more efficient, sustainable, and consumer-focused future. The continued evolution of CMC in detergent formulations is set to play a significant role in meeting the challenges of modern laundry care while adhering to environmental and safety standards.

Throughout this discussion, the integral role of Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) in enhancing the stain-removing efficiency of detergents has been thoroughly explored. CMC’s unique molecular structure and its ability to interact with, break down, and lift stains from fabrics are central to its effectiveness. Its versatility in both liquid and powder detergents and its performance in various water conditions further underscore its value in the detergent industry.
The comparison of CMC with other detergent additives highlights its superior cleaning capabilities, safety, and environmental sustainability. Innovations and ongoing research in CMC formulations indicate a commitment to improving its efficiency and reducing environmental impact, pointing towards a promising future in detergent technology.
The exploration of CMC’s role in detergents reaffirms the importance of selecting cleaning products that are not only effective but also environmentally responsible. CMC stands out as an ingredient that meets these criteria, offering a balance between high cleaning performance and environmental sustainability. As the industry continues to evolve, the continued use and improvement of CMC-based detergents will be crucial in addressing the cleaning needs of the future, while remaining mindful of our ecological footprint. This makes CMC a noteworthy and valuable component in the realm of modern detergents.





