Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC), a substance commonly used in various industries, especially in food processing, is a topic of interest for those concerned with gluten-related health issues. Understanding whether CMC contains gluten involves delving into its chemical composition, source materials, manufacturing process, and its role in food products, particularly those labeled as gluten-free.
Chemical Composition and Source
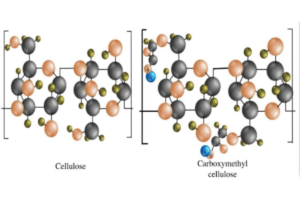
- Basic Structure: CMC is a derivative of cellulose, the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, primarily found in the cell walls of plants. Chemically, it’s known as a cellulose ether, where some of the hydroxyl (OH) groups of cellulose are substituted with carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH).
- Raw Material Sources: The primary sources of cellulose for CMC production are wood pulp and cotton lint. These sources are inherently gluten-free, as gluten is a protein found in certain grains, namely wheat, barley, and rye, and is not present in cellulose obtained from either wood or cotton.
Manufacturing Process
- Production Steps: The production of CMC involves treating cellulose with sodium hydroxide, followed by monochloroacetic acid. This chemical reaction results in the substitution of hydroxyl groups with carboxymethyl groups, rendering the cellulose water-soluble.
- Absence of Gluten in Production: Throughout this chemical process, there is no introduction of wheat, barley, rye, or any other gluten-containing materials. Hence, the process itself does not involve any gluten-containing substances.
Gluten Concerns and Cross-Contamination
- Potential for Cross-Contamination: While CMC itself is gluten-free, the potential for cross-contamination exists if it is manufactured in facilities that also process gluten-containing products. However, this risk is generally low, as CMC production typically occurs in specialized chemical plants where such cross-contamination is unlikely.
- Certification and Labeling: For individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, it’s crucial to look for gluten-free certification or labeling on products. Manufacturers aware of gluten concerns often ensure that their products, including those containing CMC, are certified gluten-free, indicating that they meet stringent standards for gluten absence.
CMC in Gluten-Free Products
- Role in Food Industry: CMC is extensively used in the food industry as a thickener, stabilizer, emulsifier, and to improve texture. In gluten-free products, it plays a vital role in substituting the texture and consistency typically provided by gluten.
- Advantage for Gluten-Free Formulations: The use of CMC in gluten-free products is advantageous as it can mimic some properties of gluten, thereby improving the quality of gluten-free baked goods, sauces, and other food products.
Conclusion
In summary, Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) does not contain gluten. Its source materials and production process are inherently free from gluten. The primary consideration for gluten-sensitive individuals would be the potential for cross-contamination, although this risk is typically minimal due to the nature of the production facilities for CMC. Consequently, CMC is a beneficial ingredient in gluten-free food products, contributing to texture and consistency without the health risks associated with gluten for those with sensitivities or celiac disease. For assurance, consumers should look for gluten-free labels or certifications, especially when dealing with severe gluten intolerances or allergies.