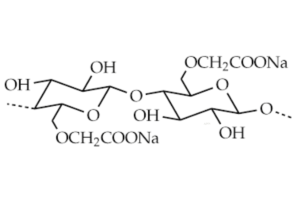
Sodium Alginate and Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) are two polysaccharide compounds widely used in various industries due to their unique chemical structures and properties. Understanding these structures and the nature of their interactions is crucial in fields like food technology, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
Chemical Structure
- Sodium Alginate:
- Source: Sodium Alginate is a natural polymer extracted from the cell walls of brown seaweed.
- Composition: It is primarily composed of two uronic acids – β-D-mannuronic acid (M) and α-L-guluronic acid (G), arranged in a block-wise manner along the polymer chain.
- Structure: The polymer chains of sodium alginate can vary in the sequence and length of the M and G blocks, influencing its physical properties. The presence of carboxyl groups (-COO-) in the alginate structure, which are ionized in the sodium form, allows it to readily interact with cations, leading to gel formation.
- Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC):
- Source: CMC is a derivative of cellulose, the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, mainly derived from wood pulp and cotton.
- Modification: It is produced by introducing carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) into the cellulose structure, a process known as carboxymethylation. This is typically done by reacting cellulose with sodium hydroxide and chloroacetic acid.
- Structure: The degree of substitution (DS), which refers to the number of hydroxyl groups on the cellulose chain that have been replaced by carboxymethyl groups, dictates the solubility and viscosity of CMC. The ionized carboxymethyl groups in sodium CMC enhance its water solubility and contribute to its ability to form gels.
Interaction Between Sodium Alginate and Sodium CMC
- Ionic Cross-Linking:
- The primary mode of interaction between sodium alginate and sodium CMC is ionic cross-linking. This occurs due to the ionized carboxyl groups present in both polymers.
- In an aqueous environment, these carboxyl groups can interact with divalent cations (like Ca^2+), leading to the formation of a three-dimensional network. This network is the basis of gel formation.
- Gel Formation and Properties:
- When sodium alginate and sodium CMC are mixed in the presence of divalent cations, each polymer can participate in cross-linking. The mannuronic and guluronic blocks in alginate interact differently with the cations, with guluronic blocks forming stronger gels.
- The interaction between these polymers can be tailored to produce gels with specific properties, like varying stiffness, porosity, and degradation rates. This is particularly valuable in applications like drug delivery and wound dressing materials.
- Synergistic Effects:
- The combination of sodium alginate and sodium CMC can exhibit synergistic effects. For instance, CMC can impart additional viscosity, enhancing the stability and handling properties of alginate gels.
- This synergism can be exploited to fine-tune the mechanical and rheological properties of the final gel for specific applications.
- Applications:
- In the food industry, these interactions are utilized to improve texture, stability, and mouthfeel of various products.
- In pharmaceuticals, the combination is used for controlled drug release, as the rate of drug release can be adjusted by manipulating the polymer network.
- In biotechnology and wastewater treatment, these gels serve as effective mediums for encapsulation and adsorption.
Conclusion
In summary, the interaction between sodium alginate and sodium CMC involves complex ionic cross-linking mechanisms, resulting from their distinct but complementary chemical structures. This interaction is crucial for creating materials with desired properties, particularly in the formation of hydrogels. The versatility of these materials, stemming from their ability to form gels with varying characteristics, makes them invaluable in a wide range of industrial applications. Understanding and manipulating these interactions allow for innovation and development of new materials and products in various sectors.