Introduction
Alginate, a naturally occurring polymer derived from the cell walls of brown seaweed, has become an indispensable material in the field of dentistry. Its unique properties, such as biocompatibility, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness, make it highly valuable for various dental procedures. Alginate’s primary function in dentistry revolves around its use as an impression material. This allows dentists to create precise molds of patients’ teeth and gums, which are essential for a multitude of treatments and prosthetic fabrications. The purpose of this article is to delve into the key applications of alginate in dentistry, providing a comprehensive understanding of its roles and benefits.
The importance of alginate in dentistry cannot be overstated. Dental professionals rely on this material for its quick setting time and accurate reproduction of the oral cavity. The ease with which it can be manipulated and its patient-friendly nature further enhance its desirability. Alginate impressions are pivotal in diagnosing dental conditions, planning treatments, and creating custom dental appliances. This introduction will set the stage for a detailed exploration of alginate’s composition, properties, and diverse applications in dental practice.
In the realm of dental materials, alginate stands out due to its unique combination of affordability and effectiveness. Its widespread use is a testament to its reliability in producing high-quality dental impressions. The versatility of alginate is another factor that contributes to its prevalence in dental clinics. From routine procedures to complex restorative and orthodontic treatments, alginate plays a crucial role in ensuring successful outcomes.
The scope of this article encompasses a thorough examination of alginate’s various applications in dentistry. By understanding the science behind this material and its practical uses, dental professionals can optimize their practices and enhance patient care. As we proceed through each section, the specific benefits and challenges associated with alginate will be highlighted, providing a balanced perspective on its role in modern dentistry.
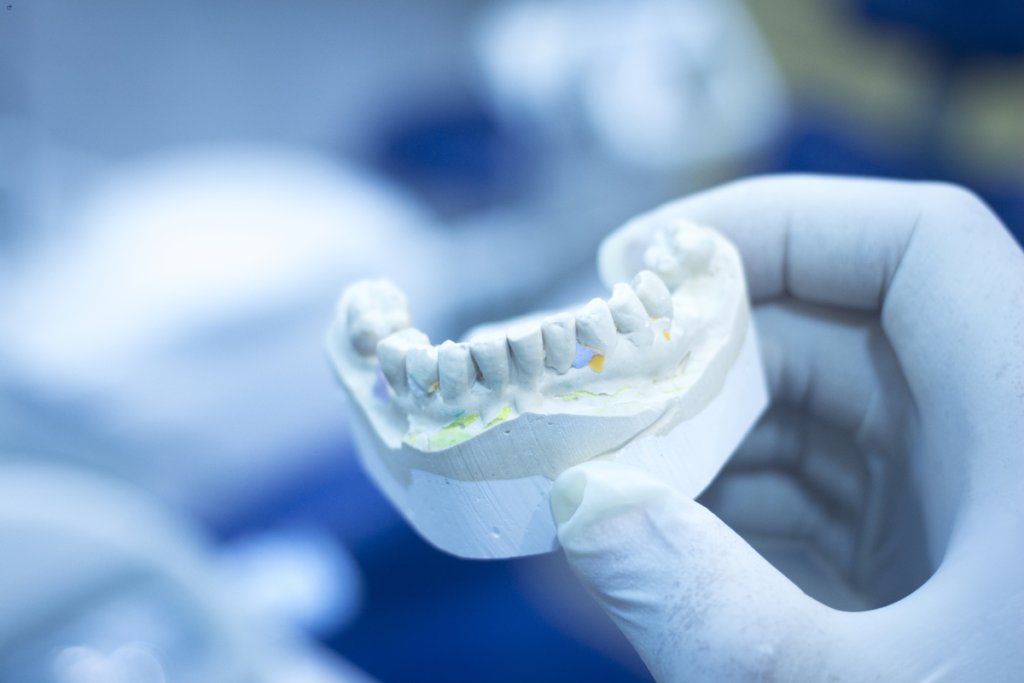
Composition and Properties of Alginate
Alginate is a naturally occurring polysaccharide extracted from brown seaweed, specifically from the cell walls of brown algae such as Laminaria, Macrocystis, and Ascophyllum species. The primary chemical constituents of alginate are mannuronic acid (M) and guluronic acid (G), which form long chains known as alginate polymers. These polymers are responsible for the gel-forming properties of alginate when it is mixed with water and a calcium-based reactant.
One of the defining features of alginate is its ability to transition from a sol (liquid) to a gel (solid) state, a process known as gelation. This occurs when the alginate is mixed with water, forming a viscous solution that quickly transforms into an elastic gel upon the addition of calcium ions. This reaction is rapid and irreversible, making alginate ideal for applications where quick setting and stability are crucial.
The physical properties of alginate include its hydrophilic nature, which allows it to absorb and retain large amounts of water, and its biocompatibility, making it safe for use in the oral cavity. Additionally, alginate exhibits excellent dimensional stability, ensuring that the impressions remain accurate and detailed throughout the dental procedure.
Several factors contribute to the suitability of alginate for dental applications:
Ease of Use: Alginate is user-friendly and can be easily mixed and applied, making it a practical choice for dental professionals. The material’s fast setting time allows for quick impression taking, which is particularly beneficial in clinical settings.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other impression materials like silicone or polyether, alginate is relatively inexpensive, making it accessible for routine dental procedures. This affordability does not compromise its performance, as alginate can produce highly accurate and reliable impressions.
Accuracy and Detail Reproduction: Alginate’s ability to accurately replicate the intricate details of the oral cavity ensures that dental prosthetics and appliances fit precisely. This precision is crucial for the success of restorative and orthodontic treatments.
Non-Toxic and Biodegradable: Being derived from natural sources, alginate is non-toxic and biodegradable, posing no harm to patients or the environment. This ecological advantage further enhances its desirability in modern dental practices.
Impression Material
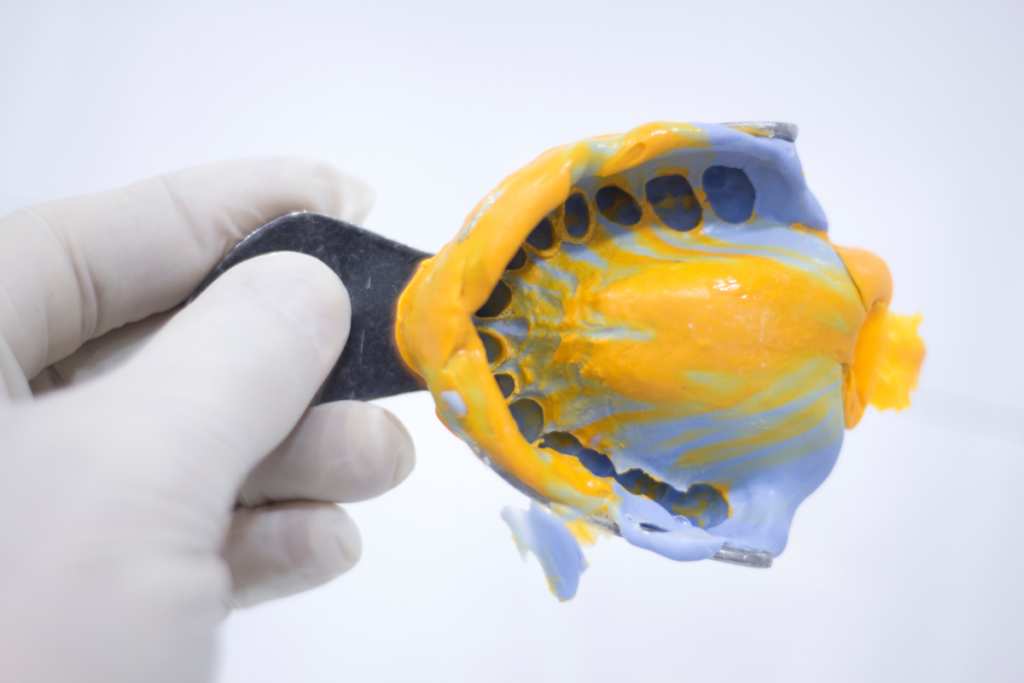
Alginate’s primary and most widely recognized application in dentistry is as an impression material. Dental impressions are crucial for creating accurate replicas of the teeth and surrounding oral structures, which are essential for various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Alginate impression material, due to its unique properties, is particularly suited for this purpose.
How Alginate Is Used to Take Dental Impressions
Taking an alginate impression involves several key steps that ensure accuracy and comfort:
- Preparation: The dental professional begins by preparing the alginate powder and mixing it with water. The ratio of powder to water is critical to achieve the desired consistency. This mixture process should be done swiftly to prevent premature setting.
- Application: Once the alginate is mixed, it is loaded onto an impression tray. The tray is then carefully placed into the patient’s mouth, covering the area that needs to be replicated. The patient is instructed to bite down gently, allowing the alginate to flow into all the nooks and crannies of the dental arches.
- Setting: Alginate has a rapid setting time, typically within a few minutes. During this time, it transitions from a gel-like consistency to a solid state. The quick setting time is advantageous as it reduces the time the patient must remain still, minimizing discomfort.
- Removal: Once the alginate has set, the impression tray is gently removed from the patient’s mouth. The alginate impression is then inspected for accuracy and completeness, ensuring all necessary details have been captured.
Advantages of Using Alginate for Impressions
Alginate impressions offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in many dental practices:
- Accuracy and Detail: Alginate is capable of capturing fine details of the oral cavity, including undercuts and subgingival areas. This precision is vital for creating well-fitting dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and dentures.
- Comfort: The smooth texture of alginate and its quick setting time contribute to patient comfort. Unlike some other impression materials that may cause discomfort or gagging, alginate is generally well-tolerated by patients of all ages.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Alginate is relatively inexpensive compared to other impression materials like silicone or polyether. This cost advantage makes it suitable for routine dental procedures without compromising on the quality of the impression.
- Ease of Use: The straightforward mixing and application process of alginate simplifies the impression-taking procedure for dental professionals. The material’s quick setting time also reduces chairside time, enhancing efficiency in dental clinics.
Applications in Various Dental Procedures
Alginate impressions are used in a variety of dental procedures, including:
- Orthodontics: In orthodontics, alginate impressions are essential for creating diagnostic models and planning treatment strategies. Accurate impressions help in designing custom orthodontic appliances such as braces and retainers.
- Prosthodontics: Alginate is widely used in prosthodontics to fabricate dentures, crowns, and bridges. Accurate impressions ensure that these restorations fit perfectly and function effectively.
- Pediatric Dentistry: The ease of use and patient comfort associated with alginate make it an ideal choice for pediatric dentistry. Children are less likely to experience discomfort during the impression-taking process, making their dental visits more pleasant.
- General Dentistry: Alginate impressions are commonly used for creating study models, diagnostic casts, and for planning various dental treatments. They provide a reliable means of documenting the patient’s dental condition at different stages of treatment.
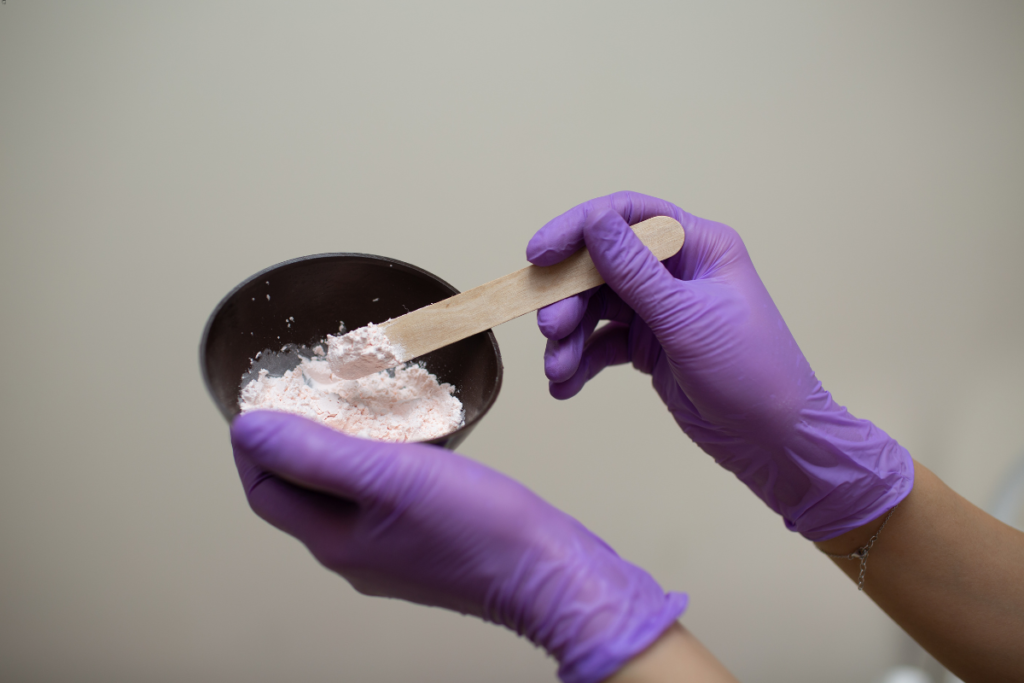
Orthodontic Applications
In the realm of orthodontics, the use of alginate as an impression material is indispensable. Orthodontic treatments aim to correct misaligned teeth and jaws, and the success of these treatments heavily relies on the accuracy and detail of dental impressions. Alginate plays a critical role in this process by providing precise molds that orthodontists use to diagnose issues and plan effective treatments.
Alginate Use in Creating Orthodontic Models
Orthodontic models, also known as study models, are three-dimensional replicas of a patient’s teeth and gums. These models are essential tools for orthodontists as they offer a clear and accurate representation of the patient’s dental structure. The process of creating these models involves several steps:
- Initial Impressions: The first step in creating orthodontic models is taking an initial impression using alginate. The alginate mixture is prepared and applied to an impression tray, which is then placed in the patient’s mouth. The patient bites down gently, allowing the alginate to flow around each tooth and capture the full dental arch.
- Pouring the Casts: Once the alginate impression is removed from the mouth and inspected for accuracy, it is used to create a dental cast. This involves pouring dental stone or plaster into the alginate mold. The material is allowed to harden, forming a solid, durable model of the patient’s teeth.
- Analysis and Treatment Planning: Orthodontists use these models to analyze the alignment and occlusion (bite) of the teeth. The detailed representation helps in identifying issues such as crowding, spacing, and misalignment. Based on this analysis, a comprehensive treatment plan is developed, which may include braces, retainers, or other orthodontic appliances.
Benefits in Orthodontic Treatment Planning
The use of alginate for creating orthodontic models offers several significant benefits:
- Accuracy and Detail: Alginate impressions capture fine details of the teeth and gums, providing an accurate base for orthodontic models. This precision is crucial for diagnosing issues and planning treatments that require exact measurements and alignments.
- Patient Comfort: Orthodontic treatments often involve young patients who may be apprehensive about dental procedures. Alginate’s quick setting time and smooth consistency reduce discomfort, making the impression-taking process more tolerable for children and adolescents.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Orthodontic treatments can be lengthy and involve multiple stages. The cost-effectiveness of alginate makes it feasible to take multiple impressions over the course of treatment without a significant financial burden.
- Versatility: Alginate is suitable for capturing impressions of both the upper and lower dental arches, as well as partial segments. This versatility allows orthodontists to obtain comprehensive data on the patient’s dental condition.
Orthodontic Appliances and Devices
Alginate impressions are foundational for the fabrication of various orthodontic appliances, including:
- Braces: Accurate alginate impressions ensure that brackets and wires are placed correctly to exert the right amount of force on the teeth, guiding them into proper alignment.
- Retainers: Post-treatment, retainers are used to maintain the new position of the teeth. Alginate impressions taken at the end of the treatment phase help in crafting retainers that fit snugly and comfortably.
- Custom Appliances: In some cases, custom orthodontic appliances like space maintainers or expanders are required. Alginate impressions provide the necessary details to create these specialized devices.
Monitoring Progress and Adjustments
Throughout the course of orthodontic treatment, periodic alginate impressions may be taken to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments. These follow-up impressions help orthodontists assess the movement of the teeth and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Adjustments to braces or other appliances can be made based on the updated models, ensuring that the treatment stays on track and delivers the desired outcomes.
Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics is a specialized field of dentistry focused on the design, creation, and fitting of artificial replacements for teeth and other parts of the mouth. This includes the fabrication of crowns, bridges, dentures, and implants. Alginate plays a pivotal role in prosthodontics due to its ability to capture accurate dental impressions, which are crucial for creating well-fitting and functional prosthetic devices.
Role of Alginate in Prosthodontic Procedures
- Initial Impressions: The first step in any prosthodontic procedure involves taking an accurate impression of the patient’s dental arches. Alginate is often the material of choice for these initial impressions because of its ease of use and quick setting time. The impressions are used to create diagnostic casts that help in evaluating the patient’s oral condition and planning the prosthetic treatment.
- Fabrication of Crowns and Bridges: Alginate impressions are used to create detailed molds of the teeth and surrounding structures. These molds are then used to fabricate crowns and bridges that fit precisely over the existing teeth or dental implants. The accuracy of the alginate impression ensures that the final prosthetic devices are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Complete and Partial Dentures: For patients who have lost multiple teeth, alginate impressions are essential for creating complete or partial dentures. The impressions capture the contour of the gum tissues and the remaining teeth, providing a detailed model for crafting dentures that fit comfortably and securely. This is especially important for ensuring that the dentures provide proper support and do not cause irritation or discomfort.
- Implant-Supported Prosthetics: In cases where dental implants are used to support prosthetic devices, alginate impressions are taken to ensure that the implants are correctly positioned and aligned with the natural teeth. The detailed impressions help in designing custom abutments and prosthetic crowns that integrate seamlessly with the patient’s existing dental structures.
Advantages of Using Alginate in Prosthodontics
- High Precision: The ability of alginate to capture fine details ensures that the prosthetic devices are crafted with a high degree of accuracy. This precision is critical for ensuring that the crowns, bridges, and dentures fit perfectly and function effectively.
- Patient Comfort: Alginate’s smooth consistency and quick setting time make the impression-taking process comfortable for patients. This is particularly important in prosthodontics, where multiple impressions may be needed throughout the treatment process.
- Cost-Effective: Alginate is a cost-effective material, making it an affordable option for both dental practices and patients. Despite its lower cost compared to other impression materials, alginate provides reliable and accurate results.
- Ease of Use: The simplicity of mixing and applying alginate makes it a practical choice for dental professionals. Its quick setting time allows for efficient workflow in busy dental practices.
Accuracy and Reliability in Prosthodontics
The success of prosthodontic treatments heavily relies on the accuracy of the impressions. Poorly fitting prosthetic devices can lead to a range of issues, including discomfort, impaired function, and even damage to the surrounding teeth and tissues. Alginate’s ability to produce precise and detailed impressions minimizes these risks, ensuring that the prosthetic devices provide optimal performance.
- Functional Performance: Accurate alginate impressions help in creating prosthetic devices that restore the patient’s ability to chew and speak effectively. Well-fitted crowns, bridges, and dentures distribute bite forces evenly, preventing undue stress on the natural teeth and supporting structures.
- Aesthetic Outcomes: In prosthodontics, achieving a natural and aesthetically pleasing result is paramount. Alginate impressions capture the exact shape and contour of the teeth and gums, enabling the creation of prosthetic devices that blend seamlessly with the patient’s natural teeth. This ensures a harmonious and visually appealing smile.
- Long-Term Durability: Prosthetic devices crafted from accurate alginate impressions tend to have a longer lifespan. Proper fit and alignment reduce wear and tear, enhancing the durability of the crowns, bridges, and dentures.
- Patient Satisfaction: The combination of comfort, functionality, and aesthetics achieved through accurate alginate impressions leads to higher patient satisfaction. Patients are more likely to adhere to their prosthetic treatments and maintain their oral health when they are satisfied with the fit and appearance of their prosthetic devices.
Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric dentistry, which focuses on the dental care of children from infancy through adolescence, often requires special considerations in terms of materials and techniques. Alginate, due to its unique properties, is particularly well-suited for use in pediatric dentistry. It offers a combination of comfort, ease of use, and quick setting time, making it an ideal choice for working with young patients who may be apprehensive or uncooperative during dental procedures.
Alginate Use in Treating Children
- Ease of Handling: One of the primary reasons alginate is preferred in pediatric dentistry is its ease of handling. Dental professionals can quickly and easily mix alginate to the right consistency and take impressions in a short amount of time. This minimizes the time the impression tray needs to stay in the child’s mouth, reducing anxiety and discomfort.
- Patient Comfort: Alginate’s smooth texture and ability to quickly set make the impression-taking process more tolerable for children. The material is less likely to cause a gag reflex, which is a common concern with young patients. Additionally, alginate impressions do not require the use of potentially irritating adhesives or chemicals.
- Versatility: Alginate can be used for a variety of purposes in pediatric dentistry. From taking initial impressions for orthodontic evaluations to creating molds for space maintainers or other dental appliances, its versatility makes it a valuable tool in treating children’s dental needs.
Comfort and Ease of Use for Pediatric Patients
The comfort of the child during dental procedures is a top priority in pediatric dentistry. Alginate’s properties contribute significantly to making dental visits less stressful and more pleasant for young patients.
- Quick Setting Time: The quick setting time of alginate is especially beneficial in pediatric dentistry. Children have shorter attention spans and may become restless if required to keep their mouths open for extended periods. Alginate’s rapid setting ensures that the impression process is completed swiftly, allowing for a smoother and faster procedure.
- Non-Toxic and Safe: Alginate is made from natural materials and is non-toxic, ensuring that it is safe for use with children. This is particularly important as children may inadvertently swallow some of the material during the impression process. Knowing that alginate is harmless provides peace of mind for both parents and dental professionals.
- Accurate Impressions: Despite the challenges that may come with taking impressions from young patients, alginate’s ability to capture fine details ensures that the impressions are accurate. This accuracy is crucial for diagnosing dental issues, planning treatments, and creating effective dental appliances for children.
Applications in Pediatric Dentistry
- Orthodontic Evaluations: Alginate impressions are often used to create diagnostic models for orthodontic evaluations. These models help in assessing the alignment of the child’s teeth and planning orthodontic treatments such as braces or expanders. Early intervention with orthodontic appliances can prevent more serious dental issues later in life.
- Space Maintainers: When a child loses a primary tooth prematurely, space maintainers are often used to hold the space open for the permanent tooth to erupt properly. Alginate impressions provide the necessary details to create these custom devices, ensuring they fit accurately and function as intended.
- Preventive and Restorative Treatments: Alginate impressions are also used in preventive and restorative treatments. For example, they can be used to create molds for fluoride trays or custom-fit mouthguards that protect the teeth during sports activities. In restorative procedures, alginate impressions help in fabricating dental crowns or fillings that restore the function and appearance of decayed or damaged teeth.
Behavioral Management
Managing the behavior of young patients is a critical aspect of pediatric dentistry. Alginate’s properties contribute to effective behavioral management by making the procedures less intimidating and more comfortable.
- Reduced Anxiety: The quick and smooth impression-taking process reduces the overall anxiety experienced by children. This positive experience can help build trust between the child and the dental professional, making future visits more manageable.
- Positive Reinforcement: Dental professionals often use positive reinforcement to encourage cooperative behavior in children. The quick and easy use of alginate allows for efficient procedures, enabling more opportunities for praise and encouragement, reinforcing good behavior during dental visits.

Comparison with Other Impression Materials
In the field of dentistry, various impression materials are available, each with distinct properties and applications. Alginate is widely used due to its favorable properties, but it is essential to understand how it compares with other commonly used impression materials such as silicone, polyether, and agar. This comparison helps dental professionals choose the appropriate material based on specific clinical needs and patient requirements.
Differences Between Alginate and Other Materials
Alginate vs. Silicone
- Composition: Alginate is a naturally derived polysaccharide, whereas silicone impression materials are synthetic and based on polymer chemistry.
- Setting Time: Alginate sets quickly, usually within 2-3 minutes, making it suitable for procedures requiring fast impressions. In contrast, silicone materials have variable setting times, which can be adjusted depending on the formulation.
- Detail Reproduction: Silicone materials, especially addition-cured (A-silicone), provide superior detail reproduction and dimensional stability over time. Alginate, while accurate, does not maintain dimensional stability as long and can distort if not poured promptly.
- Cost: Alginate is more cost-effective compared to silicone materials, which are generally more expensive due to their advanced properties and versatility.
- Usage: Silicone is preferred for final impressions in crown, bridge, and implant cases due to its accuracy and stability. Alginate is typically used for preliminary impressions, study models, and orthodontic models.
Alginate vs. Polyether
- Hydrophilicity: Polyether impression materials are highly hydrophilic, allowing for excellent detail capture in a moist environment, which is beneficial for subgingival impressions. Alginate is also hydrophilic but less so than polyether.
- Rigidity: Polyether materials are stiffer than alginate once set, providing accurate impressions but sometimes making removal from the mouth more challenging.
- Shelf Life and Storage: Polyether impressions maintain their accuracy over a longer period compared to alginate, which can dry out and distort if not used immediately.
- Application: Polyether is often used for complex restorative cases where precision is critical, whereas alginate is used for less demanding applications where quick and economical impressions are needed.
Alginate vs. Agar
- Reversible Hydrocolloid: Agar is a reversible hydrocolloid that requires a special water bath to liquefy and set the material. Alginate, an irreversible hydrocolloid, sets through a chemical reaction and cannot be reverted to a liquid state.
- Detail and Stability: Agar provides excellent detail reproduction and can be reused if needed, but it requires more equipment and time. Alginate is simpler to use but does not provide the same level of detail and must be used quickly.
- Clinical Use: Agar is primarily used in laboratory settings for duplicating models and less frequently in clinical practice due to its handling complexity. Alginate is more user-friendly for everyday clinical use.
Choosing the Right Material
The choice of impression material depends on several factors, including the specific clinical situation, the required level of detail, patient comfort, and cost considerations. Alginate remains a popular choice for preliminary impressions and situations where cost and ease of use are paramount. For more complex and precision-demanding procedures, silicone and polyether materials are often preferred due to their superior accuracy and stability.
| Property | Alginate | Silicone | Polyether | Agar |
| Composition | Naturally derived polysaccharide | Synthetic polymer | Synthetic polymer | Reversible hydrocolloid |
| Setting Time | Quick (2-3 minutes) | Variable (adjustable) | Moderate to long | Requires water bath |
| Detail Reproduction | Good but less than silicone and polyether | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Expensive | Expensive | Moderate |
| Usage | Preliminary impressions, study models, orthodontic models | Final impressions in crowns, bridges, implants | Complex restorative cases | Laboratory duplications, less clinical use |
| Hydrophilicity | Moderately hydrophilic | Moderately hydrophilic | Highly hydrophilic | Highly hydrophilic |
| Rigidity | Less rigid | Moderately rigid | Highly rigid | Moderately rigid |
| Shelf Life and Storage | Must be poured immediately, less stable | Highly stable | Highly stable | Reusable, stable |
Handling and Storage of Alginate
Proper handling and storage of alginate are crucial to ensure the material performs optimally during dental procedures. Alginate’s properties can be affected by various factors, including temperature, humidity, and mixing techniques. This section outlines best practices for handling and storing alginate to maintain its efficacy and ensure accurate dental impressions.
Best Practices for Mixing and Handling
- Mixing Ratio: It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommended powder-to-water ratio. Using the correct ratio ensures the alginate achieves the right consistency and sets properly. Typically, the ratio is measured using specific scoops and water dispensers provided by the manufacturer.
- Water Temperature: The temperature of the water used for mixing alginate significantly impacts the setting time. Cold water slows down the setting process, while warm water accelerates it. Ideally, water should be at room temperature (around 20-24°C or 68-75°F) to achieve a balanced setting time.
- Mixing Technique: The alginate powder and water should be mixed thoroughly to eliminate lumps and ensure a smooth, homogeneous mixture. This can be done manually with a spatula in a mixing bowl or using a mechanical mixer. The mixture should be smooth and creamy without any air bubbles, which can compromise the accuracy of the impression.
- Application: Once mixed, the alginate should be promptly loaded into the impression tray and placed into the patient’s mouth. Delays can cause premature setting, resulting in an inaccurate impression. The tray should be held firmly in place until the alginate sets completely.
- Removal: After the alginate has set, the impression tray should be removed gently but firmly. Care should be taken to avoid tearing or distorting the impression, which could affect its accuracy.
Storage Conditions to Maintain Efficacy
- Dry Environment: Alginate powder should be stored in a dry environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can cause premature setting or clumping. It is advisable to keep the powder in its original, tightly sealed container.
- Cool Temperature: Store alginate powder in a cool place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. High temperatures can degrade the alginate and affect its setting properties.
- Humidity Control: High humidity levels can adversely affect alginate powder. Using a desiccant or moisture-absorbing packets inside the storage container can help maintain low humidity levels.
- Shelf Life: Alginate has a finite shelf life, typically indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging. Using alginate beyond its expiration date can result in compromised performance, including improper setting and reduced accuracy. Always check the expiration date before use.
Handling of Set Impressions
- Immediate Pouring: Alginate impressions should be poured with dental stone or plaster as soon as possible, ideally within 10-15 minutes, to prevent dimensional changes. Delays in pouring can lead to shrinkage and distortion, compromising the accuracy of the impression.
- Temporary Storage: If immediate pouring is not possible, alginate impressions can be temporarily stored in a moist environment to maintain their dimensional stability. This can be done by wrapping the impression in a damp paper towel and placing it in a sealed plastic bag. However, this is only a short-term solution, and the impression should still be poured within a few hours.
- Disinfection: Alginate impressions should be disinfected before being sent to a dental laboratory. This is typically done by rinsing the impression under running water to remove saliva and debris, followed by immersion in a suitable disinfectant solution as recommended by the manufacturer.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Incomplete Setting: If the alginate does not set properly, it may be due to incorrect mixing ratios, expired material, or inappropriate water temperature. Ensuring accurate measurements and proper storage conditions can mitigate this issue.
- Tearing: Alginate impressions that tear easily may indicate an incorrect mixing ratio, insufficient setting time, or excessive force during removal. Gentle handling and following manufacturer guidelines can help prevent tearing.
- Air Bubbles: Air bubbles in the impression can occur due to inadequate mixing or improper loading of the tray. Ensuring a thorough, bubble-free mix and careful application can reduce this problem.
- Distortion: Distortion can result from delayed pouring or improper removal technique. Prompt pouring of the impression and careful removal from the mouth are essential to maintain accuracy.
Premium Quality Alginate for Dental Applications
As a leading manufacturer of alginate, we are dedicated to providing high-quality alginate products for the global dental industry. Our alginate materials are renowned for their exceptional performance and reliable stability, making them ideal for various dental applications, including orthodontics, prosthodontics, and pediatric dentistry.
Why Choose Our Alginate?
- Exceptional Precision: Our meticulously developed alginate captures intricate oral details with high accuracy, ensuring reliable dental impressions that serve as a solid foundation for dental treatments.
- Comfortable Usage: Our alginate mixes uniformly, has a smooth texture, and sets quickly, minimizing patient discomfort and making the dental professional’s job easier and more efficient.
- Superior Cost-Effectiveness: Our alginate offers excellent performance at a reasonable price, making it suitable for a wide range of dental clinics and laboratories, helping you save costs and enhance productivity.
- Stringent Quality Control: Every batch of our alginate undergoes rigorous quality testing to ensure its stability and reliability. Our production processes comply with international standards, guaranteeing the safety and effectiveness of our products.
- Eco-Friendly and Sustainable: Our high-purity alginate is derived from natural seaweed, making it environmentally friendly and safe for human use, giving you peace of mind.
Contact Us
Whether you are a dental clinic, laboratory, or dental materials distributor, we can provide you with the most suitable alginate products and professional technical support. Contact us today to learn more about our products and partnership opportunities, and together, let’s advance the dental industry.
Choose us to ensure every dental impression you make is more precise, efficient, and comfortable. We look forward to collaborating with you and creating a bright future together!






